Opinion | What Does the Recent Pig-to-Human Kidney Transplant Mean for Tissue Therapeutics?
In a pioneering procedure, a team of surgeons at New York University Langone Health Grossman School of Medicine in New...
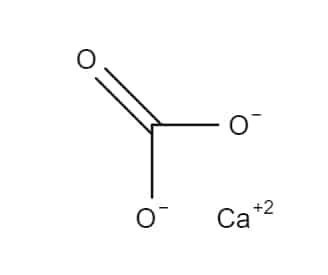
Calcium Carbonate is an inorganic mineral compound having the formula, CaCO3. It is used as a pharmaceutical excipient, antacid, and source of calcium. It may be obtained from natural sources, or through chemical synthesis. Pharmaceutical grade Calcium carbonate is supplied as an odourless and tasteless, white powder or colourless crystals.
Synonyms & Trade Names: Calcium Carbonate; Chalk; Calcite; Limestone; Synthetic Calcium Carbonate; DESTAB™; Pharma-Carb™; Precipitated Calcium Carbonate; ; Natural Ground Calcium Carbonate; E170; PCC; MagGran® Calcium Carbonate; Omyanutra® 300 DC; VITASMOOTH® Calcium Carbonate; Ground Calcium Carbonate, GCC
Pharmacopoeial Conformance: USP-NF; Ph. Eur; JP; IP; FCC
Uses & Applications: Tablet and Capsule filler and diluent; Colorant; Buffering Agent; Antacid; Source of Calcium. It is multifunctional, safe, and non-toxic excipient; monographed, low cost, widely accepted, stable (non-hygroscopic), and available in co-processed grades that are highly compactable with moderate disintegration.
Calcium carbonate is a chemical mineral substance bearing the chemical formula, CaCO3, making it a carbonic salt of calcium. It is one of the most important minerals on earth, being present in the earth’s crust (4% by weight) as well as in all living organisms. In marine animals, Calcium carbonate functions as a protective shell, and in crustaceans, it is found in the cuticle, where it serves as a reinforcing material.
Calcium carbonate is a highly versatile material. It is used as a filler, reinforcing agent, and pigment across many industries, including paper production, plastics and rubbers, inks and paints, food, cosmetics, and pharmaceutical production.
Commercial grades of Calcium carbonate are obtained via any one of the following methods:
Mechanical milling and processing of carefully-selected natural limestone ores or marble. This grade of Calcium carbonate is what is known as Ground Calcium Carbonate (GCC). GCC is used mainly as an industrial mineral filler, as well as in food and nutraceutical products as an additive and filler, depending on its particle size, colour, or purity. Highly purified grades are also available for use as excipients
Synthetically via chemical decomposition of limestone followed by recarbonisation (The Solvay Process). This grade of Calcium carbonate is known as Precipitated Calcium Carbonate (PCC). PCC is generally purer than GCC and its properties can be fine-tuned to suit particular applications.
It is important to note in n the pharmaceutical industry, both GCC and PCC grades of Calcium carbonate are available for use as excipients. Not only is there no difference in the chemical formula, but purity levels can also be matched to pharmacopoeia requirements. That stated, there are significant differences in physical properties, in particular:
For example, GCC exhibits irregular rhombohedral particles with a broad particle size distribution while PCC particles have a prismatic-rhombohedral shape and exhibit a narrow particle size distribution. The table below shows some of the excipient grades of Calcium carbonate available and their physical properties:
| particle size (d50 microns) | Surface area BET (m2/g) | Bulk Density (g/ml) | Physical Form |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 1.7 | 0.72 | Powder |
| 6 | 1.2 | 0.85 | Powder |
| 12 | 1.1 | 1.07 | Powder |
| 20 | 0.2 | 1.15 | Powder |
| Property | Identifier |
|---|---|
| Chemical Name | Calcium Carbonate |
| CAS Registration Number | [471-34-1] |
| Empirical Formula | CaCO3 |
| Molecular weight | 100.09 |
| EINCES Number | 207-439-9 |
| UNII Code (FDA) | H0G9379FGK |
Calcium carbonate is an approved pharmaceutical excipient. It is currently listed in the USP-NF, Ph.Eur, and JP. It is also GRAS listed and included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database (covering oral tablets and capsules; buccal tablets, chewing gums, and oral suspensions). Calcium carbonate is accepted for use as a food additive in Europe (E170) and a specification for Calcium carbonate is included in the Food Chemical Codex.
| Physical form | Solid, powder |
| Appearance | White powder or crystalline substance |
| Odour | Odourless |
| Solubility | Practically insoluble in water and alcohol |
| pH value (10% aqueous dispersion) | 9.0 |
| Density
Bulk Density Tapped Density Realtive |
0.8 g/cm3
1.2g/ml 2.7 |
| Compressibility | Cohesive |
| Melting point | Decomposes at 825 oC |
| Moisture content | 0.4% equilibrium moisture content at 75% RH |
| Particle size | Fine powder or granular |
| Particle shape | Orthorhombic to prismatic |
| Specific surface area | 6.21 – 6.47 m2/g |
| Thermal conductivity (cal/cm s C) | 5.6×10-3 |
| Oil Absorption | 10 |
| Dielectric Constant | 6.1 |
| USP | Ph.Eur | |
| Definition | Specified | Specified |
| Characters | Not Specified | Specified |
| Identification (Carbonates and Calcium) | Specified | Specified |
| Substances insoluble in acetic acid | ≤0.2% | ≤0.2% |
| Chlorides | Not Specified | ≤330 ppm |
| Sulfates | ≤1.0% | ≤0.25% |
| Arsenic | ≤3 ppm | ≤4 ppm |
| Barium | Specified | Specified |
| Iron | ≤0.1% | ≤200 pp, |
| Magnesium and alkali (metals) salts | ≤0.002% | ≤1.5 |
| Heavy metals | ≤0.002% | ≤20 ppm |
| Loss on drying (200 oC/4 hr) | ≤2.0% | ≤2.0% |
| Heavy metals (as Pb) | ≤0.002% | ≤20 ppm |
| Assay (CaCO3) | 98.0% – 100.5% | 98.5% – 100.5% |
| Labelling | specified | n/a |
Key: n/a Specification is not listed
*All claims with respect to conformity are subject to our Terms and Conditions. No express or implied warranty is made for specific properties or fitness for any particular application or purpose.
Calcium carbonate is a highly versatile material excipient. It is used in oral solid and liquid dosage forms both as an excipient and active pharmaceutical ingredient.
In oral solid dosage forms, Calcium carbonate functions as a filler – diluent and as a dry binder. It is widely used to formulate tablets and capsules, as well as granules and powders where the use of an inorganic, less abrasive filler-diluent is preferred over traditional fillers.
Calcium carbonate is often the preferred excipient in formulations where the active pharmaceutical ingredient is poorly soluble and/or present in low doses.
Furthermore, the chalky-soft texture in the mouth makes Calcium carbonate suitable for formulating chewable and buccal tablets and well as conventional swallow tablets produced both by wet granulation, roller compaction, and direct compression. The addition of small amounts of Calcium carbonate to tablet formulations enhances compressibility in direct compression formulations.
Three grades of Calcium carbonate are available:
A representation of how Calcium carbonate compares with other commonly used excipients is shown below:
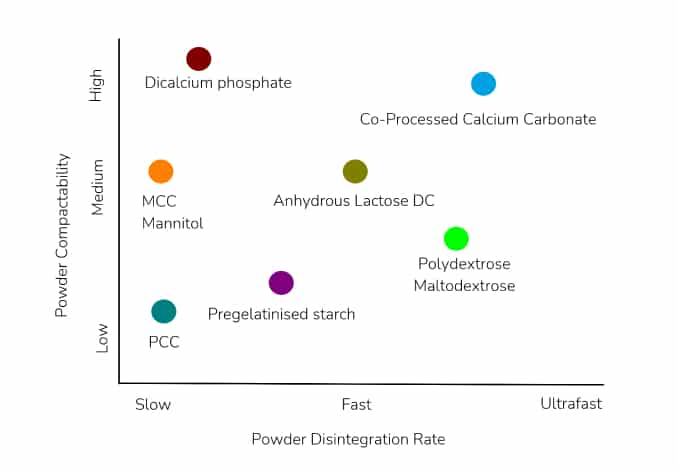
When formulating Calcium carbonate tablets, care must be taken not to exceed the daily suggested Calcium (<2.5 g per day for those under 50). It is recommended that no more than 500mg be included in a single dose. If the tablet fill weight necessitates a higher amount of Calcium carbonate to be used, this should be split, and taken 4 hours apart.
Not that higher Calcium doses (i.e >500mg) are also less bioavailable. A combination with Vitamin D can also aid the uptake of Calcium, which helps the the body utilise it more effectively.
An example of a simple tablet formulation utilising Calcium carbonate as a filler that can be processed via direct compression or wet granulation is shown below:
| Ingredient | % | Amount (g) / tablet |
|---|---|---|
| Natural calcium carbonate | 50 | |
| Vitamin K2 4500 ppm | 1.9 | |
| Vitamin D3 100000 IU/g | 0.4 | |
| Maltodextrin | 44.2 | |
| Croscarmellose sodium | 3 | |
| Magnesium stearate | 0.5 | |
| 100 |
Fine or micronized Calcium carbonate grades can be used to absorb oils or oily active pharmaceutical ingredients or other formulation additives allowing them to be transformed into dry, highly compressible powders. The higher the specific surface area, the greater the extent of oil absorption.
Many dietary supplements take the form of tablets, capsules, or stick packs. It is suitable for formulating chewable, swallow, or effervescent tablets. For tablet production, direct compaction is often the preferred approach as it is faster and more efficient.
Calcium carbonate is commonly used as a filler-diluent and dry binder in nutraceutical tablets. It offers the added advantage of providing highly bioavailable Calcium in a cost-effective and accessible format for many consumers.
Generally, highly pure, co-processed natural or ground Calcium carbonate grades are the preferred raw materials for the formulation of nutraceutical tablets. These grades are highly compressible and free-flowing, rendering them the ideal ingredient for tablet formulation.
With the exception of Calcium citrate, Calcium carbonate is preferred as a filler in nutraceutical tablets over other Calcium salts, such as Calcium phosphate, Calcium citrate, and Calcium gluconate, as its more cost-effective and more bioavailable, particularly when ingested with/after a meal due to the helpful action of gastric hydrochloric acid.
Calcium carbonate has been used as a white pigment since antiquity. It is still used as an extender in construction paints as well as a pigment in many other fields. While lacking the whiteness of titanium dioxide, it is a safer, more widely accepted material and known for its high binding and coverage properties, especially when used to formulate high solids coatings.
Speciality grades of Calcium carbonate certified to the purity requirements of the pharmacopoeia are used as sources of calcium for the treatment of osteoporosis.
Calcium carbonate is also an important active in the formulation of over-the-counter digestive aids and antacids. Being alkaline, it reacts with gastric hydrochloric acid, according to the following scheme:
CaCO3 + 2HCl -> CaCl2 + Co2 + H2O
Calcium carbonate is suitable for formulating tablets and liquids. An example of an antacid Calcium carbonate formulation is shown below:
| Ingredient | % | Amount (g) / tablet |
|---|---|---|
| Natural Calcium carbonate | 50 | |
| Povidone K90 | 3 | |
| Mannitol (DC) | 28.3 | |
| Sorbitol (DC) | 15 | |
| Orange Flavour | 2 | |
| FD&C #6 (Colour) | 0.1 | |
| Sucralose | 0.1 | |
| Magnesium stearate | 1.5 | |
| Total | 100 |
Calcium carbonate occurs freely in the natural environment and is the major constituent of limestone, marble, calcite, and aragonite. Humans and animals are ordinarily exposed to Calcium carbonate naturally dissolved in drinking water. It has been used as a food additive for several decades and is currently approved by European Food Safety Agency (Council Directive 95/2/EC) and is assigned the code E170. It is also approved for use in oral pharmaceutical products as an excipient, on the basis that it is a non-toxic, non-hazardous raw material.
The European Commission’s Scientific Committee on Food has determined that Calcium is well tolerated at a daily calcium intake of 2500 mg per day, whether it is through dietary intake or supplementation, and it does not lead to any adverse effects.
However, a number of potential side effects of excessive Calcium intake have both been described, which include:
On the basis of these and many other studies, authorities have concluded that the ingestion of Calcium carbonate by humans is tolerated at an upper intake level of 2500 mg per day (equivalent to a dose of 104 mg/kg body weight Calcium carbonate for an individual with a bodyweight of 60kg). No adverse effects are observed within this dose range.
Finally, since Calcium carbonate is used as a food additive with an ADI not allocated, the material does not create concerns regarding its toxicity when taken orally.
Calcium carbonate dust is an irritant to the eyes, nose, and mucous membranes of the airway, as well as the skin. Contact of this material with eyes can cause redness and pain, possibly due to local inflammation of cells. Thus, Calcium carbonate is hazardous when individuals become exposed through inhalation and or skin contact. The effect of temporary contact with intact skin is, however, minor.
The current permissible exposure limit for Calcium carbonate has been set at 10-15 mg/m3 of air (total dust) and 5 mg/m3 (respirable fraction) based on an 8-10 hour time-weighted average (TWA) concentrations. You can download The US Department of Health & Human Services guideline on Calcium carbonate exposure limits through this link.
When handling Calcium carbonate, you should observe precautions appropriate to the circumstances and quantity of material handled. Eye protection, gloves, and a dust mask arc are recommended. Calcium carbonate should be handled in a well-ventilated place.
Calcium carbonate nanoparticles are nanosized particles of Calcium carbonate, typically in the size range of 10 – 80 nm, and having a high surface area (30-60 m2/g). They are obtained synthetically from Calcium oxide slurries and are mainly used as reinforcing additives in plastics, industrial coatings, and imaging technologies.
Calcium carbonate nanoparticles have also been investigated as drug delivery technologies, particularly for delivery and stabilisation of protein drugs, however, there are currently no commercialised products yet.
Studies have shown that Calcium carbonate nanoparticles are biocompatible. Exposure to human cells does not show damage to cellular components, such as DNA. This suggests that these materials are probably safe for use, although more long-term studies are needed for conclusive findings.
Toxicology: LD50 (rat, oral): 6.45 g/kg
The fact that Calcium carbonate is a major constituent of minerals such as limestone and marble, which are widely present in the earth’s crust, attests to its relative stability. This also applies to Calcium carbonate excipient grade. Even though Calcium carbonate shows excellent stability under ambient conditions, it should be stored in a well-closed container, in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and water.
Calcium Carbonate may be obtained from naturally-occurring mineral ores or obtained synthetically using widely available non-critical resources. It is an inert and non-toxic excipient and considered safe for the environment, with minimal long-term impact on ecology or marine life. Calcium carbonate excipient grade achieved a total score of 76/100 by the Excipients Forum Sustainable Chemistry™ scoring scheme.
SMI (and its subsidiary, Mineral Technologies Inc) is the world’s largest producer of PCC. SMI’s grade of Calcium carbonate is supplied under the brand name:
In addition to PCC, SMI also provides GCC, which is sold under the brand name:
Magnesia GmbH is a long-established manufacturer of Calcium carbonate. The company supplies Calcium carbonate under the Magnesia™ brand, for which two PCC grades are offered:
Dr. Paul Lohmann® supplies PCC and co-processed grades of Calcium carbonate.
Imerys SA is a supplier of PCC which is marketed under the Calcius® brand name. The following grades are available:
Particle Dynamics pioneered the co-processing of Calcium carbonate with starch. The grade of readily compressible Calcium carbonate is sold under the well-known brand:
SP Pharma supplies three grades of co-processed Calcium carbonate as follows:
In a pioneering procedure, a team of surgeons at New York University Langone Health Grossman School of Medicine in New...

[bsa_pro_ad_space id=2]
[bsa_pro_ad_space id=4]
PharmaCentral.com may on occasion publish user-generated content. Any information provided on our platform is for general informational and educational purposes only. All information is provided in good faith to enable collaboration and sharing of know-how among our community of users. Authors who submit content retain copyright to it.
PharmaCentral.com does not make any representation or warranty of any kind regarding its accuracy, adequacy, or legality. Any references to particular product names, brands, descriptions, formats, styles, corporate entities, tests, applications, technologies, uses, standardisations, medical conditions, and treatments are for illustration purposes and should not be considered complete or binding. All respective intellectual property, such as trademarks and logos, are properties of their owners
Under Section 107 of the Copyright Act 1976, allowance is made for ‘Fair Use’ for purposes such as criticism, comment, news, reporting, scholarship, education, and research.
Fair use is a use permitted by copyright statute that might otherwise be infringing.
Some information contained on PharmaCentral.com may contain copyrighted material, the use of which may not have been specifically authorised by the respective copyright owners. Some material is made available to help explain and relay complex phenomena, formulae, physical and chemical constants, and other concepts that are scientifically incontestable but relevant to the use of products, and/or to illustrate, transmit, and teach pharmaceutical science principles. Some material is published to support research and user education, and for the public good.