Substances that are established components of human or animal food can, upon qualification by a scientific committee, be granted GRAS status.
For pharmaceutical excipients, GRAS status represents an interesting class of materials for product formulators since their safety profile is already considered and sufficiently known.
In this post, we will review the ins and outs of GRAS listed excipients and summarise their implications when it comes to inclusion in products, especially if they are intended for use in the United States of America.
What is the GRAS Excipients List?
“GRAS” is an abbreviation used by the US FDA for food ingredient or additives that the agency has deemed safe. It stands for Generally Recognized As Safe.
The basis for GRAS is sections 201(s) and 409 of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act, under which these substances are reviewed and approved by the FDA.
Typically, any substance that has undergone the required safety assessment by a team of experts and deemed not to cause harm when used as intended can be added to the GRAS ingredients list.
This allows the manufacturers of such materials to assign GRAS status to the material.
Alternatively, a material that was in use in the human diet before 1958, and used in such significant quantities across the population of the United States without any safety concerns. may be assigned GRAS status.
Excipients are a diverse group of ingredients other than the active ingredient(s) added to medicines, medical devices, some cosmetic products or nutraceutical food supplements.
They perform specific functions, such as promoting the product’s stability, bulk or ease of use.
Any food ingredient on the FDA’s GRAS List that is also approved for use as an excipient is a GRAS Listed excipient, provided it is manufactured and used in accordance with the provisions of sections 201(s) and 409 of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act.
Note that all excipients need to meet minimum safety requirements before they can be used in products for use by the public.
There are several certification schemes around the world, including the listing in an official pharmacopoeia, such as the United States Pharmacopoeia as well as country compendia or lists, such as the Japanese Pharmaceutical Excipients list.
Purpose of the GRAS List
The main purpose of the GRAS list is to speed up the approval and market introduction of new products and to reassure the public that the products they are consuming are safe and wholesome.
Even though the FDA has premarket approval responsibilities over food additives, a company can add an ingredient into human food products without first seeking the agency’s approval provided the ingredient has GRAS status for the intended use.
Picture a situation where regulatory agencies such as the US FDA needed to assess every ingredient de novo each time new products were launched onto the market?
Not only would this be demanding in terms of human resources for regulatory agencies but it would put strain onto new product manufacturers who would need to resubmit data on these ingredients.
Highly repetitive and unnecessary, and would slow down innovation.
Instead, having a pre-approved list of excipients permits manufacturers and scientists to create new products and meet new demands by easily incorporating these materials into their products without having to apply for fresh approvals.
History of GRAS Status
In 1958, the US Congress passed the Food Additves Amendment to the FD&C Act as a response to widescale public outcry on the rising use chemicals in food products.
The basic tenet of this law was to mandate that before any substance could be added to food products or used in food processes, companies had to demonstrate to the FDA that the substance was safe.
The FDA was required to define the conditions under which substances were to be used. Congress also stipulated mechanisms and pathways for demonstrating safetyestablished. You can read more about this topic through this link.
Suffice to say, Congress adopted a two-step definition of food additives. The first step covers substances that become components of food while the second is for substances generally recognised by experts to be safe.
GRAS Listing Process
Any material that is not a food additive and is not required to be approved through the food additive process can be added to the GRAS List provided the necessary assessments have been undertaken.
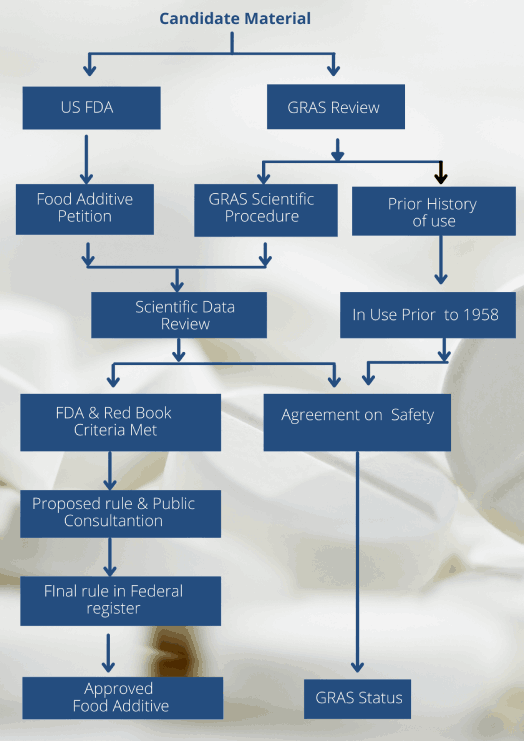
The process of GRAS listing is schematically illustrated below:
Currently GRAS Listed Excipients
There are currently just over 370 substances with GRAS status, a number of which are also approved excipients with monographs in the USP-NF, Ph.Eur or JP.
Typically, GRAS Listed excipients include natural, synthetic or semi-synthetic materials. A list of these GRAS-listed excipients, links to their descriptions and uses is shown below:
| Excipient Common Name | Pharmacopoeia Monograph | Uses and Routes of Administration |
|---|---|---|
| Acacia | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP, JP | Oral and topical products as an emulsifying agent; stabilizing agent; suspending agent; tablet binder and viscosity-increasing agent |
| Adipic acid | USP-NF, Ph.Eur | I.M injections as an acidifying agent and buffering agent. In oral products as a flavouring agent |
| Agar | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP, JP | Oral and topical products as an emulsifying agent; stabilizing agent; suppository base; suspending agent; sustained-release agent; tablet binder; thickening agent and viscosity-increasing agent |
| Alcohol (Ethanol) | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP, JP | Oral and topical products as an antimicrobial preservative and solvent. In topical products as disinfectant, skin penetrant and solvent. Approved for use in parenteral products as a solvent |
| Alginic Acid | USP-NF, Ph.Eur | Oral and topical products as a drug release-modifying agent; stabilizing agent; suspending agent; sustained release agent; tablet binder; tablet disintegrant; tastemasking agent; viscosity-increasing agent |
| Alpha Tocopherol | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP, JP | Antioxidant |
| Ammonium Alginate | FCC & FDA IIG Database | Diluent; emulsifying agent; film-forming agent; humectant; stabilizing agent; thickening agent |
| Ammonium Chloride | USP-NF, Ph.Eur | Oral products as an acidifying agent |
| Anise (Star Anise) | Ph.Eur | Oral products as a flavouring substance |
| Ascorbic Acid | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP, JP | Oral (liquids) as an antioxidant |
| Ascorbyl Palmitate | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP | Oral and topical products as an antioxidant |
| Bentonite | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP, JP | Oral products as an adsorbent/retardant for cationic drugs. In topical products as a stabilizing agent; suspending agent and viscosity increasing agent |
| Benzoic Acid | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP, JP | Parenteral products (IM & IV), oral liquids and topical products as an antimicrobial preservative |
| Butylated Hydroxyanisole | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP, JP | Parenteral products (IM & IV), topical and oral (oil-based liquids) products as an antioxidant |
| Butylated Hydroxytoluene | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP, JP | Parenteral products (IM & IV), topical and oral (oil-based liquids) products as an antioxidant |
| Butylene Glycol | FDA IIG Database | Topical products as an antimicrobial preservative; humectant; solvent; water-miscible cosolvent. In parenteral products as a solvent/co-solvent |
| Calcium Acetate | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP | Oral and topical products as an antimicrobial preservative. |
| Calcium Alginate | FCC & BPC (1973) | Oral products (liquids) as an emulsifying agent; stabilizing agent and thickening agent. As a tablet disintegrant |
| Calcium Carbonate | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP, JP | Oral products (solid dosage forms) as a buffering agent; filler and coloront in coatings; opacifier; tablet and capsule diluent |
| Calcium Chloride | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP, JP | Oral (suspensions), ophthalmic and parenterals (dry powders) as an antimicrobial preservative and desiccant. |
| Calcium Hydrogen Phosphate Anhydrous | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP, JP | Oral (tablets and capsules) as a diluent/filler |
| Calcium Hydrogen Phosphate Dihydrate | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP, JP | Oral (tablet and capsule) diluent/filler |
| Calcium Hydroxide | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP, JP | Topical and oral (suspensions) products as an alkalizing agent or pH adjuster/buffer (creams, lotions) |
| Calcium Lactate | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP, JP | Oral products as an antimicrobial preservative; buffering agent; crosslinking agent. In tablets and capsules as a diluent/filler |
| Calcium Silicate | USP-NF | Oral products as an adsorbent; anticaking agent; opacifier and diluent/filler (tablets) |
| Calcium Stearate | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP, JP | Oral products as a tablet and capsule lubricant |
| Calcium Sulfate | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP | Oral products as a tablet and capsule diluent |
| Calcium Triphosphate | USP-NF, Ph.Eur | Oral (tablets and capsules) as an anticaking agent; buffering agent; glidant and diluent/filler |
| Canola Oil | USP-NF, Ph.Eur | Topical products as an emollient; lubricant; oleaginous vehicle |
| Carnauba Wax | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP, JP | Oral products as a coating agent |
| Carob Bean gum | FCC | Topical and oral products as a stabilizer, thickener and gelling agent |
| Carrageenan | USP-NF | Oral and topical products as an emulsifying agent; gel base; stabilizing agent; suspending agent; sustained-release agent; viscosity-increasing agent |
| Castor Oil | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP, JP | Topical products as an emollient; oleaginous vehicle and solvent. In oral, parenteral and parenteral (IM) products as an oleaginous vehicle |
| Cellulose | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP, JP | Oral products (tablets and capsules) as a glidant, diluent and tablet disintegrant. In topical products as an adsorbent; suspending and thickening agent. |
| Cellulose Acetate | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP | Oral products (tablets & capsules) as a coating agent; extended-release agent and diluent |
| Citric Acid | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP, JP | Acidifying agent; antioxidant; buffering agent; chelating agent; flavor enhancer; preservative |
| Citric Acid Monohydrate | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP, JP | Oral products (tablets, gummies, liquids & coatings) as an acidifying agent; antioxidant; buffering agent; chelating agent; flavour enhancer and preservative. In parenteral and ophthalmic products as an acidifying, chelating and buffering agent |
| Corn Starch | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP, JP | Oral products (tablets & capsules) as a diluent; disintegrant and binder. In topical and liquid products as a thickening agent |
| Dextrates | USP-NF | Oral products (tablet and capsules) as a binder and diluent |
| Dextrin | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP, JP | Oral products as a stiffening and suspending agent (liquids) and binder and diluent (tablets and capsules) |
| Dextrose | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP, JP | Oral products (solids and liquids) as a tablet and capsule diluent and binder; as a sweetening and tonicity agent in liquid products |
| Disodium Edetate (EDTA) | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP, JP | Oral, topical, ophthalmic and parenteral products as a chelating agent |
| Erythritol | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP, JP | Oral solid and liquid products as sweetening and taste-masking agent. In tablet and capsule formulations as a diluent and as a platicizer in coatings |
| Erythorbic Acid | USP-NF | Oral and topical products as an antioxidant |
| Ethyl Lactate | FCC | Oral and topical products as a solvent/co-solvent for insoluble resins in emulsions. As a flavouring agent in oral liquids |
| Ethyl Maltol | FCC | Oral (liquids) products as a flavour and flavour enhancer |
| Ethyl Vanillin | USP-NF | Flavour and flavouring agent |
| Ethylcellulose | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP, JP | Oral products as a coating agent; tablet binder; tablet filler; and controlled-release excipient. In topical products as a viscosity increasing agent |
| Fructose | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP, JP | Oral products. In solid dose forms as a dissolution enhancer and diluent. In liquid dosage forms as a flavoring and sweetening agent |
| Fumaric Acid | USP-NF | Oral solid & liquid products as an acidulant and flavouring agent. In liquid products as an antioxidant |
| Gelatin | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP, JP | Oral products. In tablets as a binder, coating agent and film-forming agent. In oral liquids as a gelling agent; suspending agent and viscosity-increasing agent |
| Glucose Liquid | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP, JP | Oral products (liquids) as a sweetening agent. In oral solids as a binding liquid and coating agent |
| Glycerin | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP, JP | Oral products as an antimicrobial preservative; plasticizer; cosolvent and sweetening agent. In topical products as an emollient; humectant; solvent/co-solvent |
| Glycery Palmitostearate | FDA IIG Database | Oral products as a coating agent; gelling agent; release-modifying agent; sustained-release agent; tablet and capsule diluent. Occasionally as a tablet and capsule lubricant and taste-masking agent |
| Glyceryl Behenate | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP | Oral products as a coating agent; tablet binder and tablet and capsule lubricant. In topical products as a thickening and viscosity-increasing agent |
| Glyceryl Monooleate | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP | Topical products as an emollient; emulsifying agent; emulsion stabilizer and a nonionic surfactant. In oral products as a sustained-release agent |
| Glyceryl Monostearate | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP, JP | Topical products as an emollient; emulsifying agent; solubilizing agent and stabilizing agent. In oral products as a sustained-release agent; tablet and capsule lubricant and anti-adherent in film coatings |
| Glyceryl Triacetate (Triacetin) | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP | Oral products as a humectant; plasticizer and solvent |
| Glycine | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP, JP | Parenteral products as a buffering agent; bulking agent; dietary supplement; freeze-drying and agent. For oral products as a tablet disintegrant and wetting agent |
| Guar Gum | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP | Oral liquid products as a suspending and viscosity increasing agent. In oral solids as a tablet binder; disintegrant |
| Hydrogenated Soy Bean Oil | ||
| Hydroxyethylmethyl Cellulose | USP-NF, Ph.Eur | Oral and topical products as a coating agent; suspending agent; tablet binder; thickening agent and viscosity-increasing agent |
| Hydroxypropyl Cellulose | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP, JP | Oral products as a coating agent; emulsifying agent; thickener & stabilizing agent; suspending agent and tablet binder. Topical products as a thickening and viscosity-increasing agent. |
| Hydroxypropyl Starch | JPE | Oral products as a binding agent; disintegrant; emulsifying agent; thickening agent and viscosity-increasing agent |
| Hypromellose | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP, JP | Oral, topical and ophthalmic products as a bioadhesive material; coating agent; controlled-release agent; dispersing agent; dissolution enhancer; emulsifying agent; emulsion stabilizer; extended-release agent; film-forming agent; foaming agent; granulation aid; modified-release agent; mucoadhesive; release-modifying agent; solubilizing agent; stabilizing agent; suspending agent; sustained-release agent; tablet binder; thickening agent; viscosity-increasing agent. |
| Hydroxyethylmethyl Cellulose | Ph.Eur | Oral and topical products as a coating agent; suspending agent; tablet binder; thickening agent; viscosity-increasing agent |
| Inulin | USP-NF, Ph.Eur | Oral products as sweetening agent and tablet binder |
| Isomalt | USP-NF, Ph.Eur | Oral products as a coating agent; granulation aid; medicated confectionary base; sweetening agent; tablet and capsule diluent |
| Lactic Acid | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP, JP | Topical and oral products as an acidifying agent. Topically as a skin conditioner |
| Lactitol | USP-NF, Ph.Eur | Oral products as a sweetening agent and as a tablet and capsule diluent |
| Lactose | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP, JP | Oral, parenteral and inhalation products. In dry powder inhaler as a carrier; as a lyophilization aid in injectable products and as a tablet binder and capsule/tablet diluent/filler |
| Lauric Acid | FCC | Oral and topical products as a lubricant and as an emulsifying agent and surfactant |
| Lecithin | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP, JP | Oral, topical and parenteral products an emulsifying and solubilizing agent. As emollient in topical formulations |
| Linoleic Acid | FCC | Topical products as an emulsifying agent and skin penetrant |
| Locust Bean | Ph.Eur, BP | Oral products as a thickener; viscosity modifier; free-water binder and a suspending agent/stabilizer |
| Magnesium Carbonate | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP, JP | Oral products as an adsorbent; and as a tablet and capsule diluent |
| Magnesium Oxide | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP, JP | Oral products as a tablet and capsule diluent, anticaking agent and glidant |
| Magnesium Silicate | USP-NF, JP | Oral pharmaceutical formulations and food products as a glidant and an anticaking agent |
| Magnesium Stearate | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP, JP | Oral products as a tablet and capsule lubricant |
| Magnesium Trisilicate | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP | Oral products as a glidant. |
| Malic Acid | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP | Oral products as an acidulant; antioxidant; buffering agent; chelating agent and flavouring agent |
| Maltitol | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP | Oral (solid dosage) products as a coating agent; diluent; granulation aid and sweetening agent |
| Maltodextrin | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP, JP | Oral (solid dosage) products as a coating agent; tablet and capsule diluent and tablet binder. In oral liquid products as a viscosity-increasing agent. |
| Maltol | USP-NF | Oral (liquids) as a falvour and flavouring agent |
| Maltose | USP-NF, JP | Oral products as a sweetening agent and tablet diluent |
| Mannitol | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP, JP | Oral products as a diluent; plasticizer; sweetening agent; tablet and capsule diluent and a tonicity agent |
| Medium Chain Triglycerides | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP, JP | Oral liquid and topical products Emulsifying agent; solvent; suspending agent; therapeutic agent. In parenteral products as an oleaginous carrier |
| Menthol | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP, JP | Oral products as a flavouring agent |
| Menthyl Acetate | USP-NF, Ph.Eur | Oral products as a flavouring agent |
| Methyl Paraben | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP, JP | Oral, topical and parenteral products as an antimicrobial preservative |
| Methylcellulose | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP, JP | Oral and topical products as a coating agent; emulsifying agent; suspending agent; tablet and capsule disintegrant; tablet binder and viscosity-increasing agent. |
| Microcrystalline Cellulose | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP, JP | Oral products (tablets and capsules) as diluent, dry binder and disintegrant. In topical products as an adsorbent and suspending agent |
| Microcrystalline Wax | USP-NF | Topical products as a stiffening agent. In oral products as a controlled-release agent (added to matrix tablets) and in polymer coatings |
| Monosodium Glutamate | USP-NF | Oral products as a buffering agent and a flavouring agent |
| Myristic Acid | FCC, JPE | Oral and topical products as an emulsifying agent; skin penetrant and tablet and capsule lubricant |
| Natural Flavouring Substances | FCC | Oral products as flavourings |
| Neohesperidin Dihydrochloride | Ph.Eur, BP | Oral products as flavour enhancer and a sweetening agent |
| Oleic Acid | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP | Topical products as a emulsifying agent and skin penetrant |
| Palmitic Acid | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP | Oral and topical products as an emulsifying agent; skin penetrant; and a tablet and capsule lubricant |
| Peanut Oil | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP, JP | Parenteral products (IM) as an oleaginous vehicle. In topical products as a vehicle and solvent/carrier |
| Pectin | USP-NF | Oral and topical products as an adsorbent; emulsifying agent; gelling agent; thickening agent and a stabilizing agent. |
| Phosphoric Acid | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP | Oral, topical and parenteral products as an acidifying agent |
| Polycarbophil | USP-NF | Topical products as an emulsifying; suspending and thickening agent. In buccal, ophthalmic, nasal and vaginal applications as a bioadhesive material. In oral products as a controlled-release agent and tablet binder |
| Potassium Metabisulfite | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP | Oral products as an antimicrobial preservative and antioxidant |
| Potassium Alginate | USP-NF | Oral and topical products as an emulsifying agent; stabilizing agent; suspending agent and thickening agent |
| Potassium Alum | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP, JP | Vacines as a protein precipitant and in mouth washes/gargles as an astringent |
| Potassium Benzoate | USP-NF | Oral products as an antimicrobial preservative. Also as a tablet and capsule lubricant |
| Potassium Bicarbonate | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP | Oral products (effervescent) tablets as a source of carbon dioxide |
| Potassium Carbonate | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP, JP | Oral products as an alkalising agent |
| Potassium Chloride | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP, JP | Parenteral and ophthalmic products as a tonicity agent |
| Potassium Citrate | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP | Oral products as a alkalising agent; buffering agent and sequestering agent |
| Potassium Hydroxide | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP | Oral products as an alkalising agent |
| Potassium Sorbate | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP | Oral products as an antimicrobial preservative |
| Potato Starch | Ph.Eur; BP | Oral products as a binder and disintegrating agent |
| Pregelatinised Starch | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, JP | Oral products as a filler, binder and disintegrating agent |
| Propionic Acid | USP-NF | Oral and topical products as an acidifying agent; antimicrobial preservative; antioxidant and esterifying agent. |
| Propyl Gallate | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP | Oral and topical products as an antioxidant |
| Propyl Paraben | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP | Oral, topical and parenteral products as an antimicrobial preservative |
| Propylene Glycol | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP | Oral, topical and parenteral products as a viscosity modifier, solubiliser and plasticiser |
| Propylene Glycol Alginate | USP-NF | Oral and topical products as a solubilising, suspending and emulsifying agent. Also used in foods and cosmetics |
| Silicon Dioxide | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP | Oral and topical products as glidants, anticaking and texturizing agent. Widely used in foods and cosmetics |
| Simethicone | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP | Oral and topical products as emollient, oil vehicle and lubricant. Also as an antifoam |
| Sodium Acetate | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP | Oral, topical and parenteral products as an antimicrobial preservative, buffering agent and stabiliser |
| Sodium Ascorbate | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP | Oral and parenteral products as an antioxidant and a source of vitamin C |
| Sodium Benzoate | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP | Oral, dental, parenteral, rectal and topical products as an antimicrobial preservative |
| Sodium Bicarbonate | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP | Oral, topical, parenteral and ophthalmic products as an alkalising and therapeutic agent |
| Sodium Carbonate | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP | Oral, rectal, ophthalmic and parenteral products as a buffering and alkalising agent |
| Sodium Carboxymethylcellulose | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP, JP | Oral products as a coating agent, binder and disintegrant. For topical products as a stabilizing agent; suspending agent; and viscosity-increasing agent |
| Sodium Chloride | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP | Oral, ophthalmic, nasal, parenteral and topical products as a filler, diluent and tonicity agent |
| Sodium Citrate | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP | Oral, topical, ophthalmic and parenteral products as a buffering, alkalising and sequestering agent |
| Sodium Gluconate | USP-NF | Oral products as a natural preservative, buffer and pH adjuster |
| Sodium Lactate | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP | Parenteral, oral, topical products as an antimicrobial preservative, buffering agent, emulsifying agent and humectant |
| Sodium Lauryl Sulfate | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP | Oral, topical, rectal & vaginal products as an anionic surfactant, emulsifying agent and tablet and capsule lubricant |
| Sodium Metabisulfite | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP | Parenteral, ophthalmic, oral, rectal and topical products as a preservative and antioxidant |
| Sodium Phosphate | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP | Parenteral, oral, topical and ophthalmic products as a buffering agent |
| Sodium Propionate | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP | Oral products as a preservative |
| Sodium Stearyl Fumarate | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP | Oral products as a lubricant |
| Sodium Sulfite | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP | Parenteral, ophthalmic, oral, rectal and topical products as a preservative and antioxidant |
| Sodium Thiosulphate | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP | Parenteral, ophthalmic, oral, rectal and topical products as an antioxidant |
| Sorbic Acid | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP | Parenteral, ophthalmic, oral, rectal and topical products as a preservative |
| Stearic Acid | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP | Oral and topical products as an emulsifying and solubilising agent, and tablet and capsule lubricant |
| Sucrose | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP | Oral products as a confectionery base, coating agent, granulation binder, suspending agent, tablet and capsule binder, tablet and capsule filler, therapeutic agent, viscosity-increasing agent and sweetener |
| Sucrose Octaacetate | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP | Oral products as a bittering agent and alcohol denaturant |
| Tagatose | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP | Oral products as a sweetening agent |
| Talc | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP | Oral and topical products as an anticaking agent, glidants, tablet and capsule diluent and lubricant |
| Tapioca Starch | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP | Oral and topical products as a thickening agent, tablet and capsule diluent and disintegrating agent |
| Tartaric Acid | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP | Oral, topical and parenteral products as an acidifying agent, flavour enhancer and sequestrant |
| Thaumatin | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP | Oral products as a flavour enhancer and sweetening agent |
| Thymol | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP | Inhalation, oral and topical products as an antioxidant, antiseptic, disinfectant, flavouring and skin penetration enhancer |
| Tragacanth | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP | Oral, buccal and sublingual products as a suspending and viscosity-increasing agent |
| Trehalose | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP | Oral, inhalation and parenteral products as a flavour enhancer, humectant, stabiliser, sweetening agent, tablet diluent and thickening agent |
| Triethyl Citrate | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP | Oral products as a plasticiser and solvent |
| Urea | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP | Topical products as a moisturiser |
| Vegetable Oil – Hydrogenated | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP | Oral products as a tablet and capsule lubricant and tablet binder |
| Vitamin E Polyethylene Succinate | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, JP | Topical and oral products as an absorption enhancer; antioxidant; emulsifying agent; granulation aid; ointment base; solubilizing agent; surfactant; suspending agent; and tablet binder |
| Waxy Maize Starch | Ph.Eur, USP-NF | Oral products (tablets and capsules) as a filler/diluent, binder and disintegrant |
| White Beeswax | BP, JP, Ph.Eur, USP-NF | Oral products (tablets) as a controlled-release agent. In topical products as a stabilizing agent (emulsions) and stiffening agent (creams) |
| Xanthan Gum | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, JP, BP | Oral and topical products as a gelling agent; stabilizing agent; suspending agent; sustained-release agent and a viscosity-increasing agent |
| Xylitol | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP | Oral products as a coating agent; diluent; emollient; humectant; sweetening agent; and a tablet and capsule diluent and tablet filler |
| Yellow Beeswax | BP, JP, Ph.Eur, USP-NF | Topical products as a polishing agent; stabilizing agent and stiffening agent. In oral products as a polishing glaze for sugar coated tablets |
| Zein | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP | Oral products as a coating agent; extended-release agent and tablet binder |
| Zinc Acetate | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP | Topical products as an emollient; emulsion stabilizer; gelling agent; opacifier; stabilizing, agent |
| Zinc Stearate | USP-NF, Ph.Eur, BP | Oral products (Tablets and capsules) as a lubricant |
Is GRAS List regularly updated?
The GRAS List is constantly under review. A material on the list can indeed be removed and its status revoked by the FDA. This happened in the past when partially hydrogenated fats were removed from the list in 2015 by the FDA.
What is the SCOGS Database?
The SCOGS Database permits the public to find and read for themselves the different opinions and decisions made by the FDA and its experts (in reality, the data is limited to the period between 1972 and 1980) about the safety of over three hundred ingredients.
Click here to access the SCOGS Database.
Conclusion
So there you have it. Excipients that also have GRAS status essentially means that their use is not subject to pre-market review by the FDA for their intended use determined by an expert scientific committee.
The GRAS framework provides an additional safeguard for public welfare, by requiring manufacturers to provide information needed by regulators and consumers, regarding safety of ingredients added into consumer products.
Sources Used
To ensure our content is accurate and scientifically sound, Pharmacentral implements a strict referencing policy. We only use peer-reviewed studies and reputable academic sources and authors.
Personal opinions and anecdotes are not used.
- T.G. Neltner, N.R. Kulkarni, H.M. Alger, M.V. Maffini, E.D. Bongard, N.D. Fortin, E.D. Olson, Navigating the U.S. Food Additive Regulatory Program, Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety, 10 (2011) 342-368.
- https://www.fda.gov/food/food-ingredients-packaging/generally-recognized-safe-gras