Opinion | What Does the Recent Pig-to-Human Kidney Transplant Mean for Tissue Therapeutics?
In a pioneering procedure, a team of surgeons at New York University Langone Health Grossman School of Medicine in New...
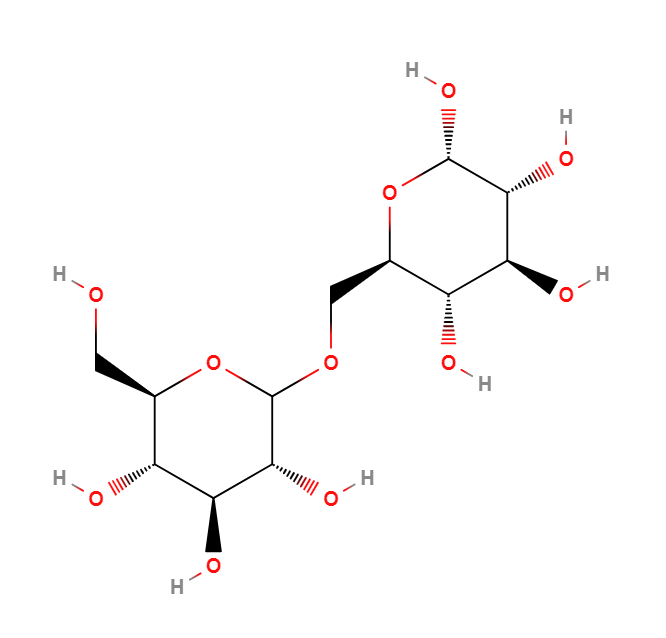
Polydextrose is a semisynthetic, low molecular weight (average molecular weight of 2000) polysaccharide excipient. It is characterised by having its glucose molecules are randomly linked within the polymer. Polydextrose is obtained through polycondensation of glucose and sorbitol, with a small amount of acid. Although all the possible glycosidic bonds are present, the 1,6 bonds dominate. Polydextrose is supplied as an off-white to light tan powder with a slightly sweet taste. It may also be supplied as a clear, light yellow or colourless liquid.
Pharmacopoeial Compliance: USP-NF
Synonyms and Trade Names: Polydextrose; E1200; STA-LITE®; Litesse®
Uses and Applications: Diluent/Bulking Agent; Coating Agent; and Binder
Polydextrose is a semi-synthetic polysaccharide polymer of glucose characterised by the presence of a high proportion of randomly bonded glucose residues. In the polymer, all possible glycosidic linkages are present, however, the 1,6 are more prevalent. It has an average DP of 12 and an average molecular weight of 2000 making it a low molecular weight polysaccharide.
Polydextrose was originally developed as a bulking agent for the food sector. Over the years, it has grown in popularity, not just within the food sector but also in the pharmaceutical field. It is also widely used across the world due to its prebiotic properties (source of dietary fibre), high thermal stability, very low-calorie content of just 1 kcal/g (4 kJ/g) and a high dietary fibre content (90% dietary fibre yield). Polydextrose is also highly water-soluble and a 70% aqueous solution exhibits a viscosity of 1800 mPa s. These features give it very favourable rheological properties that are highly sought in many processing applications.
As a pharmaceutical excipient, polydextrose is mainly used in the production of solid dosage forms. It has very low sweetness (just about 5% compared to Sucrose), is not brittle and its compressibility is similar to that of Sucrose but without the downsides. It is therefore a viable alternative to Lactose when it comes to tablet formulations (for instance, lactose replacement initiatives or nutraceutical products).
Polydextrose occurs as an odourless, off-white to light tan powder with bland, slightly sweet to slightly taste, dependent upon grade. Polydextrose is also available as a clear, light yellow to colourless liquid (70% dry substance), which is odourless with a slightly sweet taste.
| Chemical Name | Polydextrose |
| CAS Registration Number | [68424-04-4] |
| Empirical Formula | (C6H12O6)x |
| Molecular weight | 1 200 – 2 000 000 |
| EINCES Number | 614-467-9 |
| UNII Code (FDA) | VH2XOU12IE |
Polydextrose is approved as a food additive in many countries worldwide, including Europe and the USA. It is also an approved pharmaceutical excipient and is currently listed in the USP-NF and included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database. A specification for Polydextrose is contained in the Food Chemicals Codex (FCC).
| Physical state | Solid, powder |
| Appearance | Off-white to light tan powder. Polydextrose is also available as a clear, light yellow to colourless liquid (70% dry substance) |
| pH value | pH = 2.5-7.0 (10% aqueous solution). Dependent on grade |
| Particle size | % retained on 250 µm = <42% |
| Bulk density | 0.7-0.8g/cm3(dependent on grade) |
| Heat of solution | 8 kcal/g |
| Melting point | Polydextrose is an amorphous polymer that does not have a melting range. However, it softens on heating at temperatures of 150- 160 oC |
| Moisture content | 4.0% under ambient conditions. High relative humidities (>60% RH) lead to absorption of significant amounts of moisture |
| Refractive index | 1.3477 (10% w/v aqueous solution) |
| Solubility | Completely soluble in Water, Ethanol, but partly soluble in Glycerine and Propylene glycol. Polydextrose has a higher water solubility than most carbohydrates and polyols. An 80% w/w solution can be conveniently prepared (at 20 oC). Sparingly soluble or insoluble in most organic solvents |
| Viscosity | Polydextrose solutions exhibit Newtonian flow behaviour. Solutions of Polydextrose have higher viscosity than sucrose or sorbitol at equivalent temperatures. This characteristic enables polydextrose to provide the desirable mouthfeel and textural qualities that are important when formulating syrups and viscous solutions |
| USP-NF | |
| Name | Polydextrose |
| Authorised use | Excipient |
| Definition | specified |
| Characters | specified |
| Identification | A, B, C, D |
| Appearance | White or almost white, free-flowing powder |
| pH (10% solution) | 2.5- 5.0 |
| 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural and related compounds | ≤0.1% |
| Molecular weight limits | 22 000 |
| Limit of monomers
Glucose and sorbitol 1,6 Anhydrous D-glucose |
≤6.0% ≤4.0% |
| Lead | ≤0.5 µg/g |
| Residue on ignition | ≤0.3% |
| TAMC & TYMC | + |
| Assay (Dextrose polymer) | 90% |
Key: n/a Specification is not listed
*All claims with respect to conformity are subject to our Terms and Conditions. No express or implied warranty is made for specific properties or fitness for any particular application or purpose.
Polydextrose is a versatile excipient that is used in pharmaceutical products as a tablet and capsule diluent, granulation aid, humectant, binder and viscosity-increasing agent, and coating agent. Its main usage is, however, in food products where it functions as a bulking agent, texturiser, and humectant.
In tabletting operations, polydextrose solutions are used as binders in wet- granulation processes. Polydextrose solutions may also be used, in conjunction with other materials, as a film coating agent (a number of Opadry® film coatings use Polydextrose as an adjunct film former).
Polydextrose acts as a bulking agent in the formulation of sugar-free confectionary-type dosage forms. In conjunction with polyols (Isomalt, Lactitol, or Maltitol), Polydextrose is an ideal excipient in the manufacture of ‘sugar-free’ hard-boiled candies or Acacia lozenges or pastilles as a base for medicated confectionery.
Owing to the combination of high-water solubility and high viscosity of Polydextrose solutions, the processing of sugar-free candies of excellent quality is possible. Polydextrose is amorphous and does not crystallize at loss temperature or high concentrations, so it can be used to control the crystallization of po1yols and sugars, which stabilises and enhances the structure and texture of the final product.
Polydextrose has been used in food and pharmaceutical products for several decades. It is generally considered a relatively nontoxic and non-irritant product. It is approved for use as a food additive, demonstrating its acceptability across many age groups. However, when consumed in excess, Polydextrose can lead to gastrointestinal upsets owing to the high content of fibre (non-digestive carbohydrates).
In several clinical studies, the joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA) and the European Commission Scientific Committee for Food (ECSCF) concluded that polydextrose was better tolerated than other digestible carbohydrates, such as polyols. The committee concluded that polydextrose has a mean laxative threshold of approximately 90 g/day (1.3 g/kg body- weight) or 50 g as a single dose.
Toxicology profile: LD50 (rat, oral > 15g/kg, Carcinogencity: Not reported
Polydextrose powder is a hygroscopic material and has the capacity to take up moisture from the environment if not stored correctly. The reported shelf life is 36 months if correct storage conditions are followed. Solutions have shelflives of 3 to 6 months (dependent upon grade) when stored at ambient conditions.
When handling Polydextrose in an industrial setting, observe institutional SHEQ appropriate to the prevailing risk. Since Polydextrose may be an irritant to the eyes, the use of PPE (eye protection and gloves) is recommended. Suitable dust-control measures should be used.
A sustainability score for Polydextrose has not been computed by the Excipients Forum.
[4] K. Raninen, J. Lappi, H. Mykkänen, K. Poutanen, Dietary fiber type reflects physiological functionality: comparison of grain fiber, inulin, and polydextrose, Nutrition Reviews, 69 (2011) 9-21.
[5] S. Hooda, B.M.V. Boler, M.C.R. Serao, J.M. Brulc, M.A. Staeger, T.W. Boileau, S.E. Dowd, G.C. Fahey, K.S. Swanson, 454 Pyrosequencing Reveals a Shift in Fecal Microbiota of Healthy Adult Men Consuming Polydextrose or Soluble Corn Fiber, Journal of Nutrition, 142 (2012) 1259-1265.
[6] J. Slavin, Fiber and Prebiotics: Mechanisms and Health Benefits, Nutrients, 5 (2013) 1417-1435.
In a pioneering procedure, a team of surgeons at New York University Langone Health Grossman School of Medicine in New...

[bsa_pro_ad_space id=2]
[bsa_pro_ad_space id=4]
PharmaCentral.com may on occasion publish user-generated content. Any information provided on our platform is for general informational and educational purposes only. All information is provided in good faith to enable collaboration and sharing of know-how among our community of users. Authors who submit content retain copyright to it.
PharmaCentral.com does not make any representation or warranty of any kind regarding its accuracy, adequacy, or legality. Any references to particular product names, brands, descriptions, formats, styles, corporate entities, tests, applications, technologies, uses, standardisations, medical conditions, and treatments are for illustration purposes and should not be considered complete or binding. All respective intellectual property, such as trademarks and logos, are properties of their owners
Under Section 107 of the Copyright Act 1976, allowance is made for ‘Fair Use’ for purposes such as criticism, comment, news, reporting, scholarship, education, and research.
Fair use is a use permitted by copyright statute that might otherwise be infringing.
Some information contained on PharmaCentral.com may contain copyrighted material, the use of which may not have been specifically authorised by the respective copyright owners. Some material is made available to help explain and relay complex phenomena, formulae, physical and chemical constants, and other concepts that are scientifically incontestable but relevant to the use of products, and/or to illustrate, transmit, and teach pharmaceutical science principles. Some material is published to support research and user education, and for the public good.