Opinion | What Does the Recent Pig-to-Human Kidney Transplant Mean for Tissue Therapeutics?
In a pioneering procedure, a team of surgeons at New York University Langone Health Grossman School of Medicine in New...
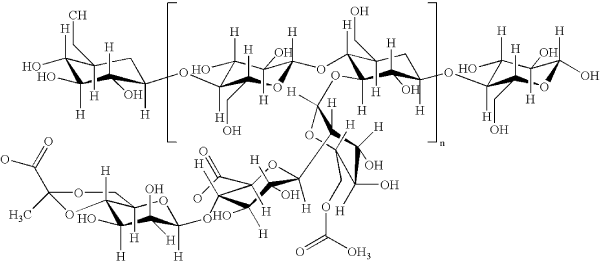
Acacia (also known as Acacia Gum or Gum Arabic) is a gum exudate from acacia trees that grow in the tropical regions of Africa. It is a complex polysaccharide formed of branched neutral-to-acidic aggregates that exist as mixed calcium, magnesium, and potassium salts. The backbone is 1,3-linked β-D-galactopyranosyl units, to which are two to five 1,3-linked β-D-galactopyranosyl units. Depending on the source, Acacia exhibits significant variability in its properties. The pharmaceutical excipient grade is usually supplied as white or yellowish-white flakes, tears, granules, powders, or spray-dried powders. It is odourless with a bland taste.
Synonyms and Trade Names: Acacia Gum; Gum Arabic; Talha Gum; E414; AGRI-SPRAY® – R
Pharmacopoeial Compliance: USP-NF; Ph.Eur; IP; FCC
Uses and Applications: Emulsifying Agent; Stabilising Agent; Tablet Binder; Viscosity-Increasing Agent, and Thickener
Acacia, also known as gum Arabic, is a natural complex polysaccharide and a pharmaceutical excipient obtained from plants of Acacia Senegal (L) or other species of Acacia. It consists of an arabic acid nucleus to which are connected calcium, magnesium, and potassium, along with the sugars arabinose, galactose, and rhamnose. The geographical areas in Africa where acacia trees grow stretch from Ethiopia to Senegal (the so-called gum belt). It has been known since antiquity and used for thousands of years as a food additive.
Acacia gum occurs as a resinous mass naturally secreted or after artificial cuts. A single tree is able to produce 400 g of gum per year. After the exudate has been dried, it is purified, graded, and sorted into different classes. To meet food and pharmaceutical specifications, the material undergoes further purification (in solution through filtration and pasteurisation).
Acacia is widely used in the food industry. In the pharmaceutical sector, there are differences in pharmacopoeial monographs. The Ph.Eur defines Acacia through different (and separate) monographs, including Acacia and Spray-dried acacia; the USP-NF describes Acacia only in a single monograph that encompasses Acacia tears, Flakes, Granules, Powder, and Spray-dried powder. The USP-NF also has a monograph on Acacia syrup. The J.P only lists two monographs: Acacia and Powdered acacia.
Pharmaceutical excipient grade acacia is supplied as white or yellowish-white thin flakes, spheroidal tears, granules, powder, or spray-dried powder. It is odourless and has a bland taste.
| Chemical Name | Acacia (17-acetyl-3,7-dihydroxy-4,4,10,13,14-pentamethyl-2,3,5,6,7,12,16,17-octahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-11,15-dione) |
| CAS Registration Number | [9000-01-5] |
| Empirical Formula | (C24H34O5) |
| Molecular weight | 240 000-580 000 |
| EINCES Number | 232-519-5 |
| UNII Code (FDA) | 5C5403N26O |
Acacia is approved for use as a food ingredient and excipient. It is also listed in all major pharmacopoeia, including the USP-NF, B.P, Ph.Eur, and the I.P. Acacia is also GRAS listed and currently accepted for use in Europe as a food additive. It is included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database (for several oral products and buccal or sublingual tablets).
| Physical form | Solid |
| Appearance | White or yellowish-white flakes, tears, powder. Aqueous dispersion are light yellow |
| Odour | Characteristic |
| pH value | pH = 4.0 – 6.5 (5% w/v aqueous solution) |
| Granulometry | Min 90% <200 µm (Spray-dried powder) |
| Solubility | Soluble in any proportion in water. Soluble in Glycerol, Propylene glycol but insoluble in Ethanol.
Hydrates slowly to produce a colourless or yellowish, viscous, gummy solution. Spray-dried grades hydrate much more rapidly (generally <30 minutes) |
| Moisture uptake | 8 – 13% equilibrium moisture uptake at relative humidities of 25-65% / 25 oC. Acacia is hygroscopic |
| Specific gravity | 1.35-1.49 |
| Viscosity (25% w/w solution, 20 oC Brookfield Viscometer) | Viscosity can vary between sources, and also depending on age, processing conditions, solution pH, and ionic composition. As concentration of the gum is raised, viscosity increases and transitions from Newtonian to non-Newtonian. |
| USP-NF | Ph.Eur | J.P | |
| Name | Acacia | Acacia | Acacia |
| Authorised Use | Excipient | Excipient | Excipient |
| Definition | specified | specified | specified |
| Identification | specified | specified | specified |
| Characteristics | specified | specified | specified |
| Glucose and fructose | n/a | specified | n/a |
| Starch, dextrin and agar | specified | specified | specified |
| Sterculia gum | n/a | specified | n/a |
| Tannins | specified | specified | specified |
| Tragacanth | n/a | specified | n/a |
| Water
Powdered Spray-dried |
≤15.0% |
≤15.0% ≤10.0% |
≤17.0% ≤15.0% |
| Total ash | ≤4.0% | ≤4.0% | ≤4.0% |
| Acid Insoluble matter | ≤0.5% | n/a | ≤0.5% |
| Arsenic | ≤3 ppm | n/a | n/a |
| Lead | ≤0.001 | n/a | n/a |
| Heavy metals | ≤0.004% | ≤1mg/kg% | |
| Microbial contamination | specified | specified | n/a |
| Assay | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| Labelling | specified | n/a | n/a |
Key: n/a Specification is not listed
*All claims with respect to conformity are subject to our Terms and Conditions. No express or implied warranty is made for specific properties or fitness for any particular application or purpose.
In the pharmaceutical industry, Acacia functions as emulsifying agent, thickener/viscosity-increasing agent, and binder, especially in buccal or lozenge type dosage forms.
Acacia powder hydrates readily in cold water and concentrations of up to 40-50% can be handled easily. Unlike other water-soluble gums of similar molecular weight, Acacia gums exhibit very low viscosity in water. For instance, a 1% dispersion of Xanthan gum yields a viscosity of 3000-5000 mPa s whereas Acacia needs a 40% concentration to achieve similar viscosity. For this reason, when used in oral and topical pharmaceutical formulations as a suspending and emulsifying agent, acacia is often combined with other gums or thickeners.
It is also used in the preparation of buccal tablets (pastilles and lozenges), and rarely as a tablet binder especially if a prolonged disintegration time is desired. It is used to stabilise oil emulsions and can be added into tablet coating formulations. At 1% Acacia gum can be used as a basis for formulating chews (hard sweets/lozenges).
Acacia is also used in topical products and cosmetics as an alternative to synthetic emulsifiers, stabilisers and thickeners.
Acacia is widely used in foods, cosmetics, and oral and topical pharmaceutical products. It is generally taken as a safe and non-toxic material. An acceptable daily intake for acacia as a food additive has not been set by health authorities since the material is not expected to be hazardous to health. However, a limited number of reports of hypersensitivity to acacia after inhalation or ingestion have been reported.
Upon ingestion, Acacia is not digested in the stomach or small intestines. Instead, it is fermented in the large intestine by the microflora into short-chain fatty acids, meaning that Acacia has prebiotic effects. It has a high tolerance effect, does not produce gas, and has no laxative effect. There have been no reported carcinogenic or teratogenic effects. The calorific value is 2 kcal/g.
Toxicology: LD50 (rat, oral): > l6g/kg; Carcigonecity: Not applicable
Acacia gum is a stable and non-reactive substance, which an expected shelf life of 3 years which can be extended subject to stability assessments. Aqueous solutions carry a negative charge and precipitate upon contact with gelatin. The high carbohydrate content means that aqueous solutions are highly susceptible to microbial attack. Measures to limit colonisation are recommended, including the addition of preservatives (Benzoic acid and Sodium benzoate (at 0.1% w/w) or a blend of Methylparaben and Propylparaben.
To ensure longevity, Acacia should be stored in a cool, dry place away from moisture and direct sunlight. When handling the powders, observe SHE precautions appropriate to the conditions of use and the amount being processed. Wearing gloves, dust masks, and eye protection are recommended since the material can irritate mucous membranes.
Acacia is a natural polymer obtained from plants. It is also an inert and non-toxic excipient and considered safe for the environment, with minimal long-term impact on ecology or marine life. Acacia excipient grade achieved a total score of 84/100 by the Excipients Forum Sustainable Chemistry Score™.
[3] K. Frimpong-Mensah, Characterization of gums from local acacia species for the food and pharmaceutical uses, Journal of the Ghana Science Association, 2 (2000) 71-79.
[4] F. Ward, Uses of Gum Arabic (Acacia sp.) in the Food and Pharmaceutical Industries, 2000.
The main uses of Acia gum are as an emulsifier and stabiliser in confectionary-type products. It is selected owing to its ability to stabilise oil emulsions. Acacia is also used in beverage products for the same reasons. In pharmaceutical and nutraceutical products, acacia gum is used as a binder and in the development of candied products (hard boiled sweets and lozenges). Acacia can also be used in softgel capsules owing to its effective emulsification (and hence, for the formulation of fish oils).
Acacia gum has been used for thousands of years as a food additive and ingredient. There are references to its use in ancient texts (e.g the Bible and ancient Egyptian texts). It is currently approved by the FAO, WHO and US FDA for use in products aimed at all ages (no limits on daily dosage).
Note that the Acacia tree is known to produce secondary substances (tannins, saponins, oxalates, hydrogen cyanide, mimosine, among others) when subjected to stress. These substances are produced by leaves and are different from the bark exudate from which Acacia gum is derived. The raw gum has vegetable and mineral impurities, and may be contaminated with bacteria. These are removed during production (washing, filtering, pasteurisation and drying).
Acacia gum powder hydrates readily in cold water. It is 100% cold water soluble. Concentrations of up to 40% can be easily handled because of their relatively low viscosity. Aqueous dispersions (<25%) exhibit Newtonian viscosity, while levels above 25% exhibit pseudoplastic rheological properties. Acacia gum solutions are stable over a wide pH range (pH 4-9) and temperature. Acacia is a complex polysaccharide (a highly-branched arabinogalactan). The constituent molecules in the polymer are galactose, arabinose, rhamnose, and glucoronic acid in a ratio of 3:3:1:1. It is resistant to normal digestion (in the stomach and small intestines) but is fermented in the large colon by bacteria into short-chain fatty acids.
Acacia gum has a total nutritional value of 200 kcal per 100 g (837 kJ), a very high fibre content (80%) and no health concerns (low glycaemic index). It is suitable for those on a ketogenic, vegetarian and vegan diet, is Halal and Kosher suitable.
In a pioneering procedure, a team of surgeons at New York University Langone Health Grossman School of Medicine in New...

[bsa_pro_ad_space id=2]
[bsa_pro_ad_space id=4]
PharmaCentral.com may on occasion publish user-generated content. Any information provided on our platform is for general informational and educational purposes only. All information is provided in good faith to enable collaboration and sharing of know-how among our community of users. Authors who submit content retain copyright to it.
PharmaCentral.com does not make any representation or warranty of any kind regarding its accuracy, adequacy, or legality. Any references to particular product names, brands, descriptions, formats, styles, corporate entities, tests, applications, technologies, uses, standardisations, medical conditions, and treatments are for illustration purposes and should not be considered complete or binding. All respective intellectual property, such as trademarks and logos, are properties of their owners
Under Section 107 of the Copyright Act 1976, allowance is made for ‘Fair Use’ for purposes such as criticism, comment, news, reporting, scholarship, education, and research.
Fair use is a use permitted by copyright statute that might otherwise be infringing.
Some information contained on PharmaCentral.com may contain copyrighted material, the use of which may not have been specifically authorised by the respective copyright owners. Some material is made available to help explain and relay complex phenomena, formulae, physical and chemical constants, and other concepts that are scientifically incontestable but relevant to the use of products, and/or to illustrate, transmit, and teach pharmaceutical science principles. Some material is published to support research and user education, and for the public good.