Dextrin Excipient | Uses, Suppliers, and Specifications
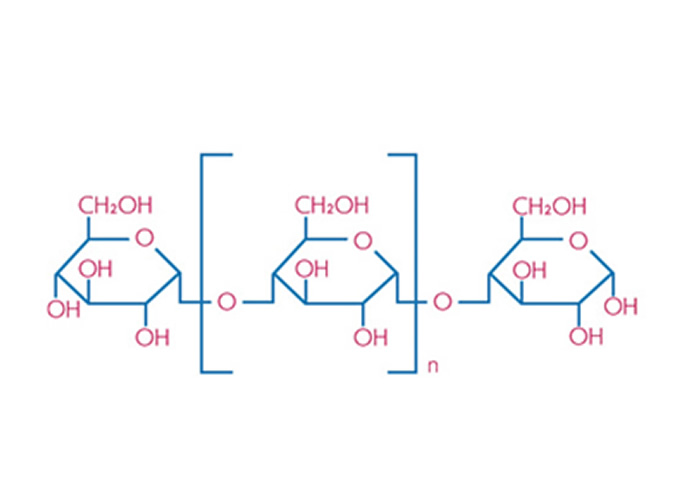
Dextrin is a generic term applied to a variety of low molecular weight carbohydrate polymers obtained by partial hydrolysis of starch. Dextrin has the general chemical structure of (C6H10O5)n and molecular weights typically between 4500 and 85 000, depending on the number of (C6H10O5) units in the polymer chain.
Pharmaceutical grade dextrins are obtained from maize (corn), potato or cassava starch and occur as a white, pale yellow or brown-coloured powder with a slight characteristic odour.
Physicochemical Properties
| Physical form | Solid, powder |
| Acidity/alkalinity | pH = 2.8—8.0 for a 5% w/v aqueous solution |
| Density (bulk) | 0.80 g/cm3 |
| Density (tapped) 1 | 0.91 g/cm3 |
| Density (true) | l.495—1.589g/cm3 |
| Melting Point | 178 oC (with decomposition) |
| Flash Point | 477 oC |
| Moisture content | 5% w/w |
| Particle size distribution | Varied |
| Solubility
|
Slowly soluble in cold water and very soluble in boiling water, forming a mucilaginous solution. Practically insoluble in ethanol (95% and propan-2-ol |
| Specific surface area | 0.14 m2/g |
Pharmaceutical Applications
Dextrin is a suspending agent; tablet binder; and a tablet and capsule diluent. It is used as an adhesive and stiffening agent for surgical dressings. In tablet and capsule formulations, dextrin is used as a diluent; as a binder for tablet granulation; as a sugar-coating ingredient that serves as a plasticizer and adhesive; and as a thickening agent for suspensions.
In addition, dextrin has been used as a source of carbohydrate by people with special dietary requirements because it has a low electrolyte content and is free of lactose and sucrose.
Pharmacopoeia Specifications
| Test | Specification | Reference |
| Identification | + | USP-NF/PhEur |
| Appearance | White or almost white, free-flowing powder | USP-NF/PhEur |
| pH | 2.0- 8.0 | USP-NF/ PhEur |
| Chlorides | + | USP-NF/PhEur |
| Reducing Sugars | + | USP-NF/PhEur |
| Heavy Metals | ≤10ppm | USP-NF/PhEur |
| Loss on Drying | ≤13.0% | USP-NF/PhEur |
| Sulphated Ash | ≤0.5% | USP-NF/PhEur |
Safety and Regulatory Status
Dextrin is listed in the PhEur, USP-NF and JP. It is GRAS listed and included in the FDA Inactive ingredients Database (IV injections, oral tablets and topical preparations). Dextrin is generally regarded as a nontoxic and non-irritant material at the levels employed as an excipient. Larger quantities are used as a dietary supplement without adverse effects, although ingestion of very large quantities may be harmful.
LD50 (mouse, IV): 0.35 g/kg
Stability and Storage Conditions
The physical characteristics of dextrin vary depending on the method of manufacture and the material’s source. In aqueous solutions, dextrin molecules tend to aggregate as density, temperature, pH or other characteristics change. An increase in viscosity is caused by gelation or retrogradation as dextrin solutions age, and is practically noticeable in the less-soluble maize starch dextrins.
Dextrin solutions are thixotropic, becoming less viscous when sheared but changing to a soft paste or get when allowed to stand. However, acids that are present in dextrin as residues from manufacturing can cause further hydrolysis, which results in a gradual thinning of solutions. Residual acid, often found in less soluble dextrins can also cause a reduction in viscosity during dry storage. To eliminate these problems, dextrin manufactures neutralize dextrins of low solubility with ammonia or sodium carbonate in the cooling vessel.
The bulk material should be stored in a well –closed container in a cool, dry place.
Handling Precautions
Observe normal precautions appropriate to the circumstances and quantity of material handled. Dextrin may be irritant to the eyes. Eye protection, gloves, and a dust mask are recommended.
References
[1] G.H.P. Te Wierik, A.C. Eissens, C.F. Lerk, Preparation, characterization and pharmaceutical application of linear dextrins: IV. Drug release from capsules and tablets containing amylodextrin, International journal of pharmaceutics, 98 (1993) 219-224.
[2] G.H.P. Te Wierik, A.C. Eissens, C.F. Lerk, Preparation, characterization and pharmaceutical application of linear dextrins: V. Study on the binding properties of amylodextrin, metastable amylodextrin and metastable amylose, International journal of pharmaceutics, 102 (1994) 81-90.
[3] M. Lederer, E. Leipzig-Paganini, Dextrin as excipient in pharmaceutical preparations, Die Pharmazie, 55 (2000) 378-379.
[4] K. Alvani, X. Qi, R.F. Tester, Use of carbohydrates, including dextrins, for oral delivery, Starch‐Stärke, 63 (2011) 424-431.