What are Ion Exchange Resins?
Ion Exchange Resins (IER) are synthetic pharmacopoeia grade water insoluble cross-linked polymers that contain a salt-forming group at regular positions on the polymer chain and have the capacity to exchange counter-ions in aqueous solution.
IERs were developed in the 1930s for water purifications applications. In the 1950s, they were introduced in the pharmaceutical industry as APIs and excipients. Currently, IERs are varyingly utilised as pharmaceutical excipients for controlling drug release agents (matrix tablets), solubility enhancement, increasing stability, taste masking and abuse deterrents.
Although there are many grades of IERs, only two materials currently meet official compendial requirements and are widely recommended for use in products. These are Polacrilin Potassium NF and Sodium Polystyrene Sulfonate USP-NF.
Selection and Grades of IERs
| Polacrilin Potassium NF | Sodium Polystyrene Sulfonate USP | |
| Chemical Description | Potassium salt of a cross-linked copolymer of methacrylic acid and divinylbenzene | Sodium salt of a sulfonated copolymer of styrene and divinylbenzene |
| Physical Form | White, fine or granular powder | White, fine powder |
| Pharmacopoeia | USP-NF | USP-NF |
| Solubility | Insoluble | Insoluble |
| Hygroscopicity | Hygroscopic | Hygroscopic |
| Type | Weak acid | Strong acid |
| Functional Group | -COO- | -SO3– |
| Exchangeable Cation | Potassium | Sodium |
| pH Dependence | Yes | No |
| Commercial Grades | AMBERLITE™ IRP88 (Dow)
KYRON T-134 (Corel Pharma) |
AMBERLITE™ IRP69 (Dow)
KYRON T-154 (Corel Pharma) |
Advantages of IERs
- IERs are highly versatile – they can be used in most oral drug delivery systems, including ODTs, tablets, chewable and effervescent tablet, capsules as well as dry syrups and liquid suspensions.
- IERs can significantly improve safety and patient adherence by helping mask bitter tastes, improve bioavailability and reduce pill burden
- IERs have a long history of use – spanning over 50 years of safety data.
- IERs are simple to use – they do not require major changes to equipment or processes.
How to use IERs for Taste Masking
IERs provide an effective means to bind the bitter active principle onto an insoluble matrix via a simple ion exchange reaction. The reaction is a reversible, selective and stoichiometric exchange of ionic species that have similar charges.
The wet taste-masked complex can be used for suspension formulation directly. Alternatively, it can be dried and used in tablet, capsule or dry syrups.
The process of using IER for taste masking could not be any easier. There are two main ways to load the drug (API) on to the EIR: column method and batch method. The column method involves passing a highly concentrated solution of the API through a column of resin particles until equilibrium complexation is achieved. The batch process involves agitating a solution of the drug with a quantity of the IER until equilibrium complexation is achieved.
Generally, the batch method is preferred as it is simple and straightforward. A predetermined amount of drug is loaded onto the IER, the quantity added mainly influenced by the cation exchange capacity (which is a measure of an IER’s ability to hold exchangeable cations and therefore bind the API). The other factors that influence loading are the IER’s selectivity for the API, particle size, porosity and degree of crosslinks.
To start, it is important to identify the most ideal IER for the API. If not sure, consult your supplier for guidance. However, a simple screening process can be done that involves preparation of 1% w/v API solution to which the IER is added in different ratios, e.g 1:1, 1:2, 1:3, etc. The blends are stirred for up to 20 hours and sample solutions taken at regular interval in order to assay for free, uncomplexed drug. The most suitable IER is then one with the lowest amount of free drug (concentration remaining in solution).
The process is illustrated below:
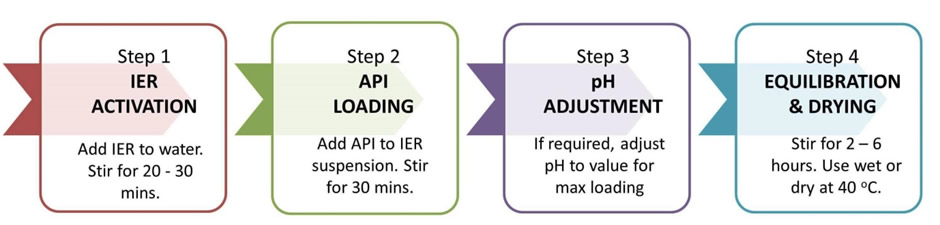 Once the equilibration is completed, the IER-API complex can be washed, and used as is in syrups and suspensions or dried and blended with other excipients and compressed into tablets of choice or filled into capsules.
Once the equilibration is completed, the IER-API complex can be washed, and used as is in syrups and suspensions or dried and blended with other excipients and compressed into tablets of choice or filled into capsules.
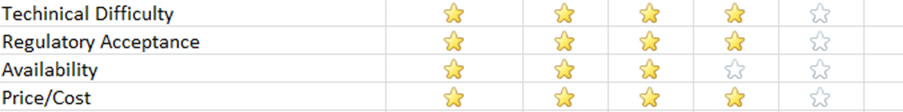
Usability Rating
Martel, J. J et al., 1981. Acid type ion Exchange resins and their use as medicines and compositions containing them. Patent EP27768.
Felton, L. A., 2018. Use of polymers for taste-masking pediatric drug products. Drug Devt Ind. Pharm 44, 1049 – 1055.