Potassium Sorbate | Uses, Suppliers, and Specifications
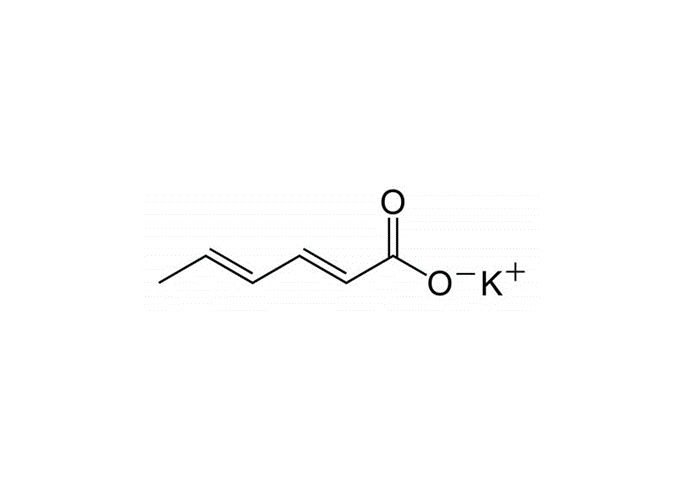
Potassium sorbate, otherwise referred to as potassium (E,E)-hexa-2,4-dienoate, is the potassium salt of sorbic acid. It occurs as a white crystalline powder with a faint, characteristic odour.
Physicochemical Properties
| Physical state | Solid |
| Density | 1.363 g/cm3 |
| Solubility | Soluble in water and other aqueous solvents. Water solubility is 58.2 g/100 ml |
| Melting Point | 270 °C |
| Antimicrobial activity | predominantly used as an antifungal preservative, although it also has antibacterial properties. |
| Melting point | 270with decomposition |
Application in Pharmaceutical Formulation
Potassium sorbate is an antimicrobial preservative It exhibits both antibacterial and antifungal properties used in pharmaceuticals, foods, enteral preparations and cosmetics. Generally, it is used at concentrations of 0.1 – 0.2% in oral and topical formulations, especially those containing non-ionic surfactants.
Potassium sorbate is used in approximately twice as many pharmaceutical formulations as is sorbic acid owing to its greater solubility and stability in water. Like sorbic acid, potassium sorbate has minimal antibacterial properties in formulations above pH 6.
Potassium sorbate has been used to enhance the ocular bioavailability of timolol.
Pharmacopoeial specifications
| Test | Specification | Reference |
| Identification | A, B, C, D | USP-NF/PhEur |
| Appearance | White or almost white powder or granules | USP-NF/PhEur |
| Appearance of solution | + | USP-NF/PhEur |
| Aldehydes | + | USP-NF/ PhEur |
| Heavy metals | ≤10ppm | USP-NF/PhEur |
| Loss on drying | ≤1.00% | USP-NF/PhEur |
| Assay | 99.0 – 101.0% |
Safety and Regulatory Status
Potassium sorbate is listed in the USP-NF, PhEur and JPE. It is GRAS listed and included in the FDA inactive ingredients database (nasal sprays; oral capsules, solutions, suspensions, syrups, tablets; topical creams and lotions). Accepted for use as a food additive in Europe.
Potassium sorbate is used as an antimicrobial preservative in oral and topical pharmaceutical formulations and is generally regarded as a relatively nontoxic material. However, some adverse reactions to potassium sorbate have been reported, including skin irritation, which may be of the allergic, hypersensitive type. There have been no reports of adverse systemic reactions following oral consumption of potassium sorbate.
The WHO has set an estimated total acceptable daily intake for sorbic acid, calcium sorbate, potassium sorbate, and sodium sorbate expressed as sorbic acid at up to 25mg/kg body-weight
LD50 (mouse, IP): 1.3g/kg
LD 50 (rat, oral): 4.92g/kg
Stability and Storage Conditions
Potassium sorbate is more stable in aqueous solution than sorbic acid; aqueous solutions may be sterilized by autoclaving.
The bulk material should be stored in a well closed container, protected from light, at a temperature not exceeding 40. Some loss of antimicrobial activity occurs in the presence of nonionic surfactants and some plastics.
Handling Precautions
Observe normal precautions appropriate to the circumstances and quantity of material handled. Potassium sorbate is irritant to the skin, eyes and mucous membranes; eye protection and gloves are recommended. In areas of limited ventilations, a respirator is also recommended.
References
[1] E. Lueck, Antimicrobial Food Additives: Characteristics, Uses, Effects, 1980.
[2] D.S. Orth, Establishing cosmetic preservative efficacy by use of d-values, J. Soc. Cosmet. Chem, 31 (1980) 165-172.
[3] J.N. Sofos, F.F. Busta, Antimicrobial Activity of Sorbate, Journal of Food Protection, 44 (1981) 614-622.
[4] J.N. Sofos, Sorbate Food Preservatives, 1989.
[5] S.P. Denyer, R.M. Baird, Guide to Microbiological Control in Pharmaceuticals, 1991.
[6] F.F. Morpeth, Preservation of Surfactant Formulations, 1995.
[7] H.W. Rossmoore, Handbook of Biocide and Preservative use, 1995.
[8] D.K. Brannan, Cosmetic Microbiology: A Practical Handbook, 1997.
[9] B.M. Lund, T.C. Baird-Parker, G.W. Gould, Microbiological Safety and Quality of Food, 1999.
[10] L. Jimenez, Microbial Contamination Control in the Pharmaceutical Industry, 2004.
[11] A. Cremieux, S. Cupferman, C. Lens, Method for evaluation of the efficacy of antimicrobial preservatives in cosmetic wet wipes, International Journal of Cosmetic Science, 27 (2005) 223-236.
[12] C. Boukarim, S. Abou Jaoude, R. Bahnam, R. Barada, S. Kyriacos, Preservatives in liquid pharmaceutical preparations, J Appl Res, 9 (2009) 14-17.
[13] T. Angelov, The Parabens, Very Close to the Ideal Drug Preservatives, 2014.
[14] J.E. Simmons, Fluid Preservation: A Comprehensive Reference, 2014.